When you need to remove a subject from its background, you’ll often encounter two terms – clipping path and image masking. While both serve the same ultimate goal—isolating a subject to place it on a new background—they are fundamentally different tools for different jobs.
Choosing the wrong technique can lead to a sloppy, unprofessional result that hurts your brand’s image. So, how do you know which one is right for your photos?
This comprehensive guide will provide a clear, side-by-side comparison of clipping path vs. image masking. By the end, you’ll understand the core differences and know exactly which method to use for your specific needs, whether you’re a photographer, a graphic designer, or an e-commerce business owner.
What is a Clipping Path?
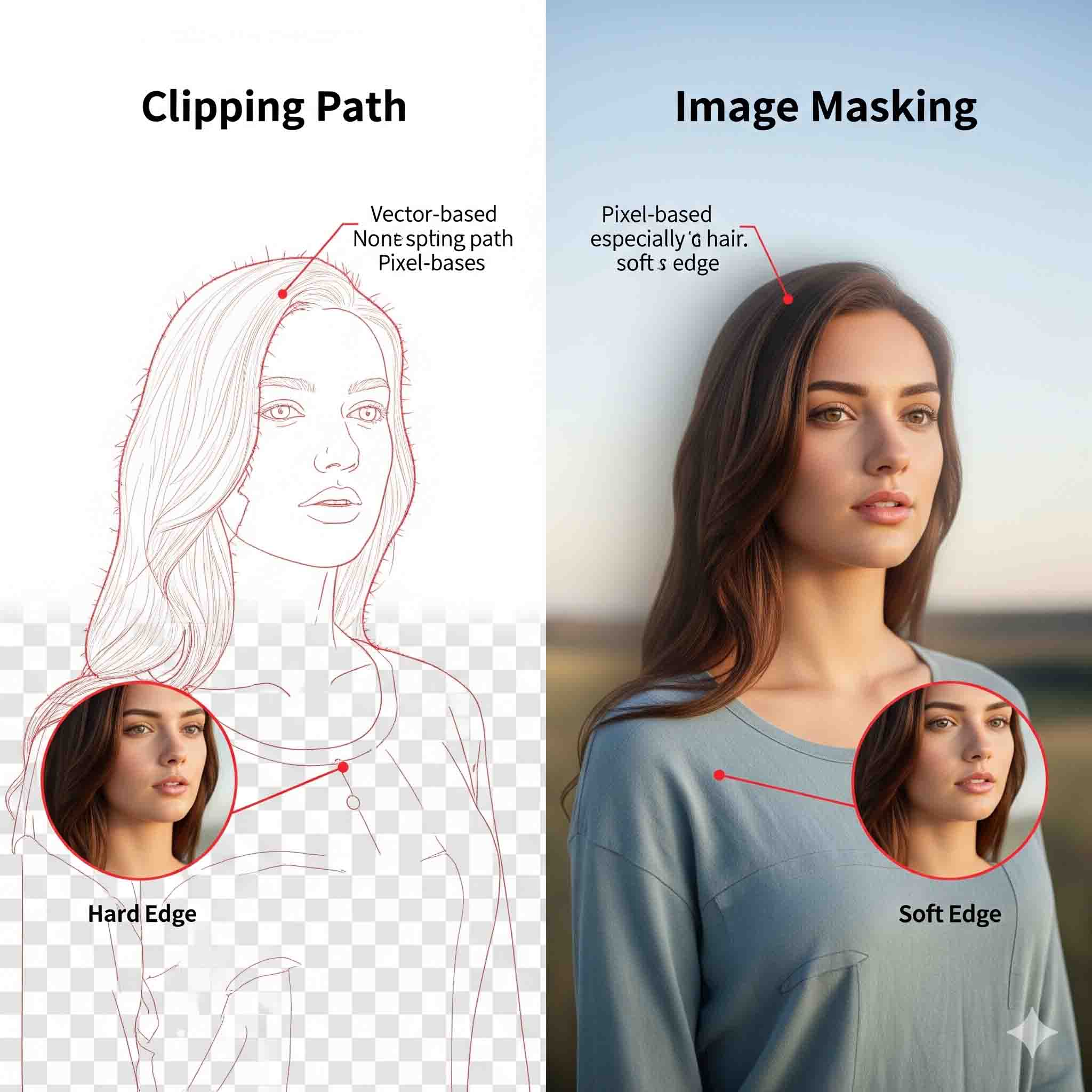
A clipping path is a vector-based selection created with the Pen Tool in Adobe Photoshop. Think of it as a hard-edged, custom-drawn outline around an object. Because it’s a vector path, it creates a perfectly crisp and sharp selection.
This technique is best for subjects with solid, well-defined edges. It’s the go-to method for creating clean, professional cut-outs that look excellent on any background.
Key Characteristics
- Vector-based: Uses mathematical lines and curves, not pixels.
- Hard Edges: Creates a razor-sharp separation between the subject and the background.
- Tool: Primarily created with the Pen Tool.
Best Use Cases (with real-world examples):
A clipping path service is perfect for products with clean, sharp lines.
- Product Photography: Electronics, furniture, shoes, books, and boxes.
- General Photography: Vehicles, buildings, or any object with a straight or simple curved outline.
What is Image Masking?
Image masking is a pixel-based technique that is much more sophisticated than a clipping path. Instead of creating a hard, vector-based line, it uses a Layer Mask to non-destructively hide parts of an image. This allows for the precise selection of complex or soft edges, including semi-transparent areas.
This technique is essential for subjects that a simple clipping path cannot handle. It’s what professional photo editors use to achieve seamless, natural-looking cut-outs.
Key Characteristics
- Pixel-based: Works with the individual pixels of an image.
- Soft & Complex Edges: Ideal for intricate details and delicate textures.
- Non-Destructive: The original image data is preserved, allowing for edits at any time.
- Tools: Relies on tools like the Select and Mask workspace, Channels Palette, and the Brush Tool.
Best Use Cases (with real-world examples):
An image masking service is a necessity for subjects with a lot of fine detail.
- People: Especially for subjects with intricate, flyaway hair.
- Animals: For subjects with fine fur or feathers.
- Delicate Fabrics: Lace, sheer curtains, or semi-transparent clothing.
- Translucent or Transparent Objects: Glassware, bottles, smoke, water, or lighting effects.
Clipping Path vs. Image Masking: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Clipping Path | Image Masking |
| Method | Vector (Pen Tool) | Pixel (Layer Mask/Channels) |
| Edge Quality | Hard, sharp, defined | Soft, intricate, detailed |
| Ideal For | Subjects with straight lines or simple curves | Subjects with complex details like hair or fur |
| Output File Type | EPS, sometimes JPEG | PSD, PNG (for transparent backgrounds) |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; a static path | Highly flexible; non-destructive |
| Common Uses | Shoes, furniture, electronics | People, furry animals, glass objects |
The Best of Both Worlds: When to Use Both
Sometimes, a single image may require the precision of both a clipping path and an image mask. For example, imagine a product shot of a model wearing a hat and a sheer dress.
- The hard edges of the hat and any accessories would be best selected with a clipping path.
- The soft, delicate textures of the hair and the sheer fabric of the dress would be perfected using image masking.
A professional background removal service often uses a combination of both techniques to deliver a flawless result that no single method could achieve.
Conclusion: The Right Tool for the Job
The choice between clipping path and image masking boils down to one simple question: What is the complexity of your subject’s edges?
If your subject has clean, sharp lines, a clipping path is the efficient and effective solution. If it has intricate, soft, or transparent details, image masking is the only way to achieve a professional result. By understanding this key difference, you can ensure your product photos are always crisp, clean, and perfectly suited to impress your customers.
Looking for expert photo editing that uses the right technique every time? Explore our professional clipping path and image masking services today for a perfect result on all your products.